Retirement Accounts Unraveled: 401(k) vs. IRA
When it comes to planning for retirement, understanding the different types of retirement accounts available can be overwhelming. From 401(k)s to IRAs, there are a multitude of options to choose from. However, breaking down the differences between a 401(k) and an IRA can make the decision-making process much simpler.
Let’s start by defining what exactly a 401(k) and an IRA are. A 401(k) is a retirement account typically offered by employers, where employees can contribute a portion of their paycheck on a pre-tax basis. This money is then invested in a variety of options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, with the goal of growing the funds over time. On the other hand, an IRA, or Individual Retirement Account, is a retirement account that individuals can open on their own through a financial institution. Like a 401(k), contributions to an IRA can grow tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement.
One of the key differences between a 401(k) and an IRA is who can contribute to each type of account. With a 401(k), contributions are typically made by the employee through automatic payroll deductions, although some employers may also make contributions on behalf of the employee. In contrast, an IRA is funded solely by the individual, and contributions are usually made on a voluntary basis.
Another important distinction between a 401(k) and an IRA is the contribution limits. For 2021, the annual contribution limit for a 401(k) is $19,500 for individuals under the age of 50, while those over 50 can make catch-up contributions of an additional $6,500. In comparison, the annual contribution limit for an IRA is $6,000 for individuals under 50, with an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000 for those over 50.
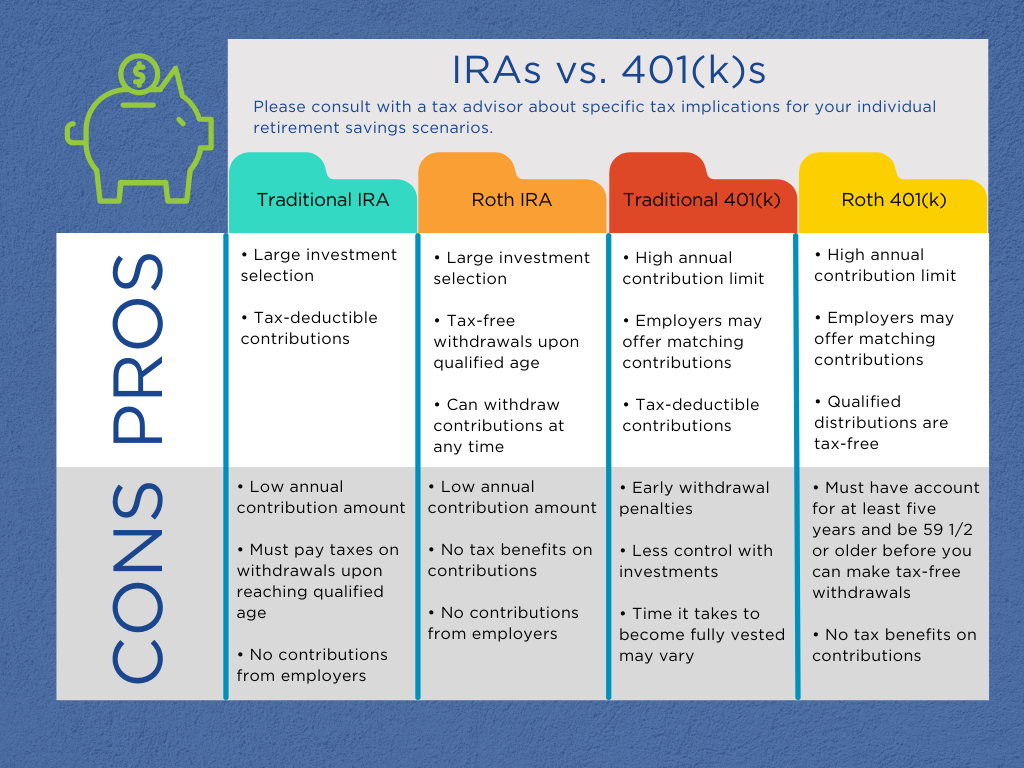
Image Source: sccu.com
When it comes to investment options, 401(k)s and IRAs also differ in terms of flexibility. With a 401(k), investment options are typically limited to a selection chosen by the employer. On the other hand, an IRA offers a wider range of investment choices, allowing individuals to tailor their investments to their specific financial goals and risk tolerance.
One of the benefits of a 401(k) is that some employers offer matching contributions, meaning they will match a certain percentage of the employee’s contributions up to a specified limit. This essentially provides free money towards retirement savings, making a 401(k) a valuable tool for building a nest egg for the future. However, not all employers offer matching contributions, so it’s important to check with your employer to see if this benefit is available.
On the other hand, one of the advantages of an IRA is the ability to choose from a wider variety of investment options. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who are looking to diversify their retirement savings and take a more hands-on approach to investing. Additionally, IRAs offer more flexibility in terms of contributions, as individuals can open and contribute to an IRA even if they are not eligible for a 401(k) through their employer.
In summary, both 401(k)s and IRAs offer valuable benefits for retirement savings, but they cater to different needs and preferences. A 401(k) may be a good option for individuals who have access to an employer-sponsored plan with matching contributions, while an IRA may be more suitable for those who are looking for a wider range of investment options and greater flexibility in contributions. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on your individual financial situation and retirement goals.
Breaking Down Retirement Accounts: 401(k) vs. IRA Made Simple
Deciphering the World of Retirement Savings
Retirement may seem like a distant dream for some, but it’s never too early to start thinking about your future financial security. One of the key components of a solid retirement plan is understanding the different types of retirement accounts available to you. Two popular options are the 401(k) and the IRA, each with its own set of benefits and considerations. Let’s dive into the world of retirement savings and break down these two important accounts.
First up, let’s talk about the 401(k). This employer-sponsored retirement account is a common option for many working professionals. One of the biggest advantages of a 401(k) is that contributions are made pre-tax, meaning you can lower your taxable income while saving for retirement. Additionally, many employers offer matching contributions, which is essentially free money added to your retirement savings. It’s like getting a bonus every time you contribute to your 401(k)!
On the other hand, an IRA, or Individual Retirement Account, is a retirement savings account that you open on your own. There are two main types of IRAs: traditional and Roth. A traditional IRA offers tax-deferred growth, meaning you won’t pay taxes on your earnings until you withdraw them in retirement. On the other hand, a Roth IRA offers tax-free growth, meaning you pay taxes on your contributions upfront, but your withdrawals are tax-free in retirement.
So, how do you decide between a 401(k) and an IRA? It ultimately depends on your individual financial situation and goals. If your employer offers a 401(k) with matching contributions, that can be a great way to maximize your retirement savings. However, if you’re self-employed or your employer doesn’t offer a 401(k), an IRA can still be a valuable tool for saving for retirement.
One key difference between a 401(k) and an IRA is the contribution limits. For 2021, the contribution limit for a 401(k) is $19,500, with an additional catch-up contribution of $6,500 for those over 50. On the other hand, the contribution limit for an IRA is $6,000, with an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000 for those over 50. So if you’re looking to maximize your retirement savings, a 401(k) may be the way to go.
Another factor to consider is investment options. With a 401(k), your investment options are limited to what your employer offers in their plan. This can be both a positive and a negative, as it simplifies the decision-making process but may limit your ability to customize your investment strategy. On the other hand, an IRA offers more flexibility in terms of investment options, allowing you to choose from a wide range of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
Regardless of which type of retirement account you choose, the most important thing is to start saving for retirement as early as possible. The power of compound interest means that the more time your money has to grow, the better off you’ll be in retirement. So whether you opt for a 401(k), an IRA, or both, make sure to prioritize your retirement savings and take advantage of any employer matching contributions available to you.
In conclusion, understanding the world of retirement savings can seem daunting at first, but with a little research and planning, you can set yourself up for a comfortable and secure retirement. By breaking down the differences between a 401(k) and an IRA, you can make an informed decision about which option is best for your financial goals. Remember, it’s never too early to start saving for retirement, so take the time to explore your options and make a plan that works for you. Your future self will thank you!
Retirement Accounts Explained: 401(k) vs. IRA